Introduction
The root canal anatomy of the maxillary first molar has been extensively reviewed in the literature, revealing that this tooth may present a great variation in root canal configurations, mainly in the mesiobuccal canal. The prevalence of a second mesiobuccal (MB2) canal for type 2 (2-1) was found 42% in males and 37% in females; for type 4(2) was found in 29% and 27% males and females, respectively. However, the prevalence of a MB3 canal is infrequent.1
A substantial amount of literature exists on second mesiobuccal (MB) canals in first and second maxillary molar.2 However, existence of three canals in the MB root is rare, reporting an incidence of 0.6%–4.2% clinically.3 Clinically, a third MB canal was first reported by Martínez-Berna and Ruiz-Badanelli in the maxillary first molar.4
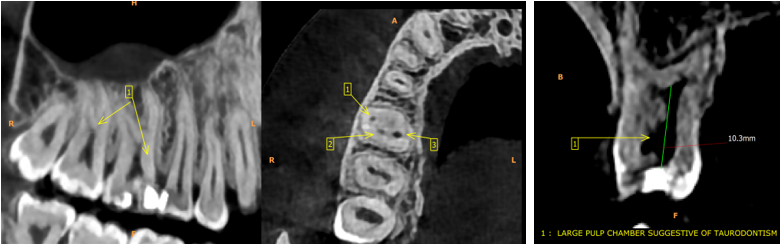
On the contrary, Taurodontism is a morpho-anatomical change that usually appears in the form of multi-rooted teeth. The affected teeth have proportionately shortened roots, and their pulp chambers are enlarged as a result of apical prolongation.5
This rare case report depicts the presence of a third MB canal (MB3) in a maxillary right first molar, with a Vertucci's Type VIII canal configuration, i.e., three independent canals on one side and Mesotaurodontim on the contralateral arch.
Case Report
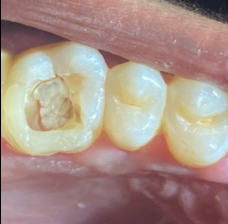
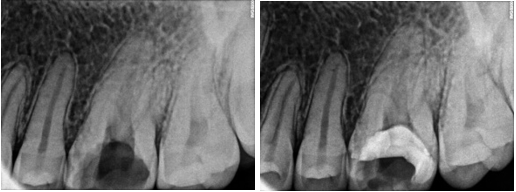
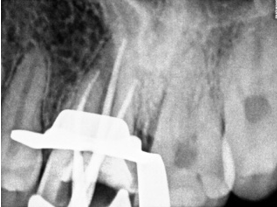
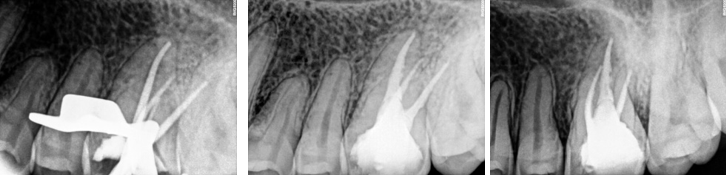
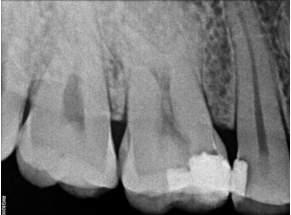
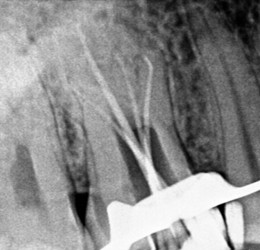
A 25 years old male patient was referred to the clinic for the treatment of maxillary right and left first molar tooth. Patient reported the complaint of pain on biting or pressure in upper right and left back teeth region from past 1 week. History dates back to 4 months when patient first experienced pain in upper right back teeth region. He visited local dental surgeon for the same whereby root canal treatment was initiated in #16 which was not completed due to some unavoidable family circumstances (Figure 1). Also, he had undergone restoration in #25, 26. Cold test and electric pulpal testing showed a delayed response suggesting irreversible pulp damage. Clinical and radiographic inspection revealed an upper right first molar with good dental structure and the presence of a teflon tape (Figure 1) that invaded the pulp chamber with widening of PDL space around the apex of tooth #16 (Figure 6) while tooth #26 showed composite restoration close to pulp. Clinical and radiographic examination lead to a diagnosis of previously initiated with symptomatic apical periodontitis in #16 (Figure 6) and Irreversible pulpitis with normal apical tissues in #26 (Figure 16) indicating the need for endodontic treatment.
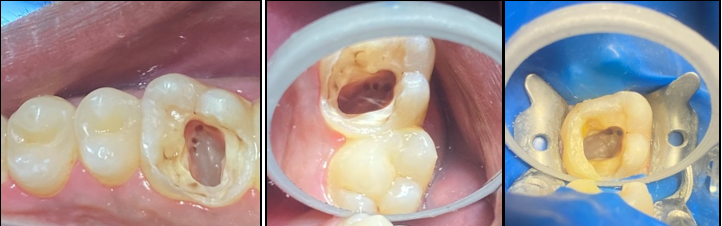
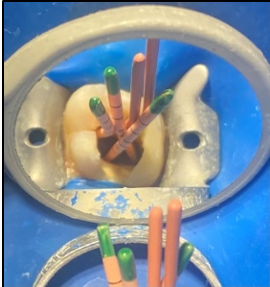
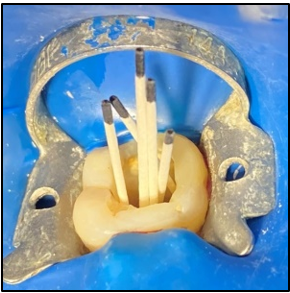
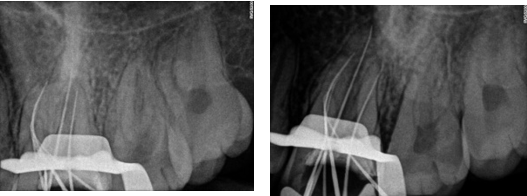
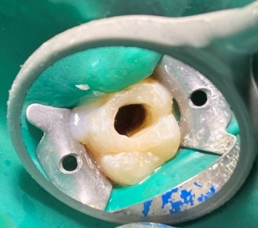
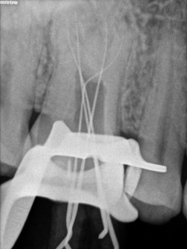
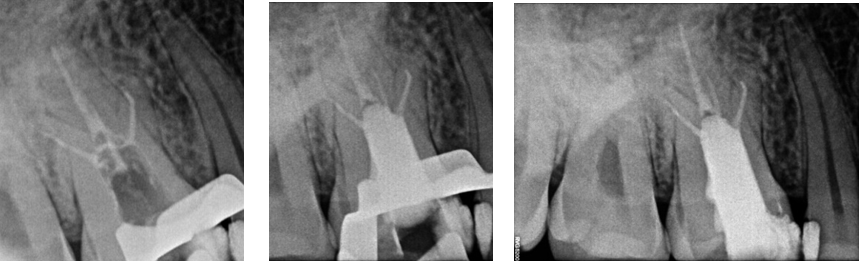
In the first appointment, the complete treatment plan, benefits & risks were explained to the patient & consent was taken prior to the commencement of the treatment. The tooth was anesthetized using 2% articaine with 1:200 000 epinephrine followed by rubber dam isolation and access opening was made using Endo Access Bur (Figure 2). The working lengths of all five canals were estimated by means of an electronic apex locator (Coltene) and were found to be 18 mm in MB1, MB2, and MB3; 19 mm in DB; and 20.5 mm in P canal, respectively, which was then confirmed radiographically using different angulations (Figure 7). Glide path was prepared up to a size 20, 0.02 taper, in all five canals using stainless steel hand K-files, followed by rotary instrumentation with NiTi HyFlex CM files to a size of 25, 0.04 taper (MB2,MB3) and 35, 0.04 taper (MB, DB, P).
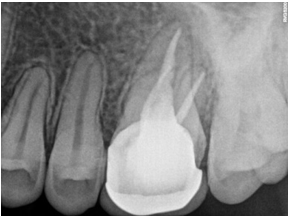
The canals were irrigated with one ml of 2.5% sodium hypochlorite per canal per instrument change. Normal saline was used to flush out the NaOCl, following which 17% EDTA was used for smear layer removal followed by calcium hydroxide dressing for 1 week. In the subsequent appointment, calcium hydroxide was removed and copious irrigation with saline was done. The canals were dried with paper points (Figure 4). All the canal walls were then coated with AH Plus sealer and obturated using a single-cone technique with the Gutta-Percha of corresponding sizes of the rotary files used (Figure 3, Figure 8).
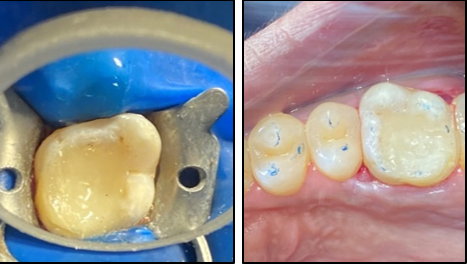
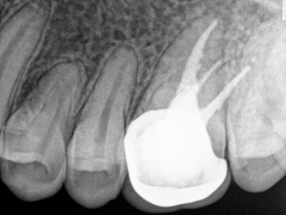
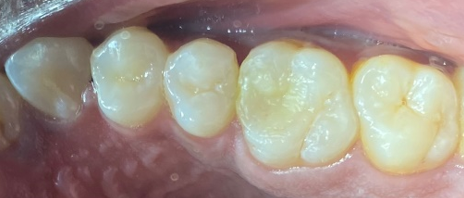
The access cavity was restored with composite in the same visit and occlusion was checked (Figure 5, Figure 9). On follow-up visit, Porcelein-fused to metal crown was given to the patient after 1 month (Figure 10) followed by follow-up examination after 6 months (Figure 11).
Discussion
A study on taurodontism has mentioned that it is frequently associated with hereditary or genetic malformations.[16] In this case, however, the patient was a healthy male with no known diseases. This condition is, then, considered to be an anatomic difference that can occur in the normal population.6 Clinical instrumentation of maxillary first molar tooth, especially with respect to the MB root and in cases of taurodontism can be complicated.7 Failure to detect and treat the MB2 and MB3 canal system will result in a decreased long-term prognosis. CBCT is a useful device for evaluating root canal anomalies and can also be used for intra- or post-operative assessment of treatment complications.8
Conclusion
This report shows that the clinician must be conscious of anatomic variations during the diagnostic and treatment phases of maxillary first molars, so that correct root-canal therapy can be performed respecting the possible challenges of pulp space anatomy. The frequency of maxillary first molars with 5 root canals especially with three MB canals and Mesotaurodontism is rare; however, each case should be investigated carefully, clinically and radiographically, to detect the anatomical anomaly.