- Visibility 47 Views
- Downloads 8 Downloads
- DOI 10.18231/j.johs.2024.016
-
CrossMark
- Citation
Forensic odontology: A dental detective’s perspective from central India
- Author Details:
-
Mayank Chandrakar *
Introduction
Forensic science is scientific method of collection and examining information about the past which is then used in a court of law. Forensic science can play vital role in a judicial setting and accepted by the court and general scientific community to separate truth from untruth. [1], [2] Forensic identifications are multidisciplinary team efforts that essentially involve the coordination and cooperation of Policeman, Lawyers, forensic pathologists, forensic odontologists, forensic anthropologists, serologists, criminalists and other specialists.[3]
Forensic sciences generally is used for solving Medicolegal Case. Judiciary in India is facing complex problems right now leading to abnormal delays in doing justice; nearly 4.7 Crore cases are undecided in the Indian courts. [4] So a common man feels halting to approach the Police Stations or Law Courts and when they become sufferer of crime or injustice.
Forensic Odontology is application of dental knowledge in criminal and civil cases that are imposed by Policeman in legal system. [5], [6], [7] Forensic is derived from the Latin word forum, which means “court of law”. Odontology refers to study of teeth. Forensic Odontology has been described by the Federation Dentaire International as that branch of dentistry which, in the interest of justice, deals with the proper handling and examination of dental evidence and with the proper evaluation and preservation of dental findings.[8], [9]
Forensic odontology is an important and intrinsic part of forensic science. This is chiefly used for identification of living and deceased persons. Today, forensic odontology has developed as a new ray of hope in assisting forensic medicine. Though this is in infancy state in India as comparison to developed countries of the world like U.S.A. and U.K. There Forensic Odontology has considered a recognized branch of dental surgery in Forensic Medicine. [3]
Forensic Odontology comprises identification of human remnants through dental records at the scene of crime, child or adult abuses[10] and determines age and sex of the living or deceased for presenting forensic dental testimony as a witness in a court.[11] In forensic odontology, tooth prints, radiographs, dental photographs and investigations like rugoscopy and cheiloscopy are used.[12], [13] DNA fingerprinting is an excellent method for accurate forensic diagnosis.[14], [15]
Dental identification has a decisive role in the identification of remains when post-mortem changes, traumatic tissue injury or lack of fingerprint record negates use of visual or fingerprint methods. The tooth has been used as weapons in identification of biter. Teeth are the most stable parts in the body and can be heated to temperature of 1600°C without appreciable loss of microstructure.[16], [17]
Dental identification has played a significant in natural as well as manmade disasters. Natural (Earthquake, Drought and Tsunami) or man-made disasters (Terrorism, Homicides and Suicide Bombing) can lead to loss of lives of millions of people internationally.[18], [19], [20]
Crimes oftenly associated with biting are homicide, rape, sexual assault, robbery and child abuse. The crime type, age and sex of the subject impact on the likely anatomical location of a bite injury. Bite marks will assist to solve the crime. Bite marks give not only information about the dental characteristics of the criminal but also their psychological background.[21]
India has a fantastic history of forensic science. Application of science and technology for detection and investigation of crime and administration of justice is well known to us. Its detailed allusion is found in ‘Kautilya's Arthashastra’ 2300 years ago. Papillary lines (‘Rugoscopy’) were studied thousands of years ago by Indians. First case of identification from India was of Raja Jayachandra Rathore of Canouj, who died on the battlefield in 1191 and his body was identified by his false anterior teeth. Forensic Odontology had been applied successfully in the case of the assassination of the former Prime Minister of India, Mr. Rajiv Gandhi. [22] A forensic odontologist from Dharwad, Dr. Asith B Acharya helped Police in solving NewDelhi Gang Rape Case 2012. [23] Forensic odontology has play remarkable role in Sheena Bora murder case (2012). In this case Sheena was murdered and her body was buried three years ago but forensic experts identified her from skull and tooth.[24]
At present, natural and man-made disasters are occurring more oftenly in India with increasing crime like sexual assault and child abuse. There can be difficulty of recognition of mangled body, So Dental Surgeon's role is crucial in identification of body. Dental expert can help Police Personnel in solving criminal cases. There is need of formal training of Police Personnel in forensic science. Before undertaking the dental expert opinion Police Personnel have to investigate principally regarding dental involvement in crime and preserve dental testimony. Hence Forensic Odontology is of preeminent importance to all Police Personnel.[5], [6], [7] In India under sections 174 and 176 Cr.P.C., only police and magistrate inquests are done and they are public servants with very less exposure to law and forensic science throughout their professional training. Policemen and Judges are scientifically lay individuals. There are difference in agencies in India who do crime scene investigation and autopsy and other scientific investigations. One remarkable feature is these agencies are working alone, with less coordination. [25] Considering above facts in mind a questionnaire study had done to evaluate the knowledge of Forensic Odontology among Policemen of Mahasamund.
Materials and Methods
This questionnaire survey was conducted from 5 February 2022 to 7 February 2022 in Policemen of District Police Headquarter of Mahasamund for assessment of knowledge of Forensic Dentistry. Survey schedule for data collection had made. On an average 45 Police Personnel were interviewed face to face per day.
This study’s ethical clearance was obtained from Ethical Committee of Rungta Dental College, Bhilai. Incharge of District Police Headquarter, Mahasamund gave permission for doing study among Policemen. A written informed consent was taken from every participant before the study.
A self administered questionnaire was given to every participants. Both male and female Policemen took active participation. The validity of the questionnaires were assessed by both Dental Surgeon and Policemen.
A total of 133 Police Personnel, available at the time of study and agreed to participate formed the final sample.
Inclusion criteria
Policemen who were available at the time of study and who gave consent for participation were included.
Exclusion criteria
Police Personnel who were absent on the day of study because of their duty.
Police Personnel who did not give consent and who were not willing to participate.
Proforma
A self-administered questionnaire consisted of 19 questions in which 3 questions were open ended questions. The questionnaire comprised information about Demographics, Basic knowledge of Forensic Science, Basic knowledge of Forensic Dentistry, Dental Identifications, Abuse, Bite Mark Evidence and Criminal Litigations. The questionnaire and consent forms are made in Hindi language and used in survey.
Statistical analysis
SPSS software package version 18.0 was used for analysis of collected data and Descriptive statistics was recorded. Associations between overall knowledge of forensic odontology and experience, sex, rank and education of Police Personnel were tested using Chi-square test. p-value less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant in our study.
|
|
Frequency |
Percentage |
|
Constable |
82 |
61.70% |
|
Head Constable |
21 |
15.80% |
|
Assistant Sub Inspector |
10 |
7.50% |
|
Sub Inspector |
10 |
7.50% |
|
Inspector |
10 |
7.50% |
|
Total |
133 |
10000% |
|
|
Frequency |
Percentage |
|
Middle School Certificate |
1 |
0.80% |
|
High School Certificate |
11 |
8.30% |
|
Intermediate or Post School Diploma |
61 |
45.90% |
|
Graduate or Post Graduate |
60 |
45.10% |
|
Total |
133 |
100.00% |
|
Question Number |
Question |
Options |
Frequency |
Percentage |
|
1 |
Do you know what is Forensic Science? |
Yes |
133 |
100% |
|
No |
0 |
0% |
||
|
2 |
Do you know Forensic Science help is sought by Police in solving cases for investigations? |
Yes |
111 |
83.50% |
|
No |
22 |
16.50% |
||
|
3 |
Do you know Forensic Dentistry is a part of Forensic Science? |
Yes |
110 |
82.70% |
|
No |
23 |
17.30% |
|
Question Number |
Question |
Options |
Frequency |
Percentage |
|
4 |
Have you had any formal training in evaluating dental evidence? |
Yes |
0 |
0% |
|
No |
133 |
100% |
||
|
5 |
Do you know that Forensic Odontology can be used for identification of victims? |
Yes |
77 |
57.90% |
|
No |
56 |
42.10% |
||
|
6 |
Do you know that Forensic Odontology can be used for determination of age and sex of victims? |
Yes No |
84 49 |
63.20% 36.80% |
|
7 |
In what situations Forensic Odontology is useful in criminology? |
Age determination |
19 |
14.30% |
|
D.N.A. |
29 |
21.80% |
||
|
Bite Marks |
37 |
27.80% |
||
|
All of the above |
48 |
36.10% |
|
Question Number |
Question |
Options |
Frequency |
Percentage |
|
8 |
Do you know about dental identification marks which can be used for identification of victims? |
Yes |
70 |
52.60% |
|
No |
63 |
47.40% |
||
|
9 |
Do you know importance of saliva in victim’s identification? |
Yes |
47 |
35.30% |
|
No |
86 |
64.70% |
||
|
10 |
Do you know that D.N.A. analysis can be done using person’s teeth? |
Yes |
62 |
46.60% |
|
No |
71 |
53.40% |
||
|
11 |
Do you know role of dental prosthesis in identification of dead persons in Mass Disaster? |
Yes |
54 |
40.60% |
|
No |
79 |
59.40% |
||
|
Question Number |
Question |
Options |
Frequency |
Percentage |
|
12 |
Do you know importance of Dental Photography in Abuse and Domestic Violence cases? |
Yes |
52 |
39.10% |
|
No |
81 |
60.90% |
|
Question Number |
Question |
Options |
Frequency |
Percentage |
|
13 |
Do you know about Bite Marks? |
Yes |
30 |
22.60% |
|
No |
103 |
77.40% |
||
|
14 |
What is Bite Marks? |
Correct Answer |
14 |
46.67% |
|
Wrong Answer |
16 |
53.33% |
||
|
Total |
30 |
100% |
||
|
15 |
In what way Bite Marks help? |
Correct Answer |
8 |
26.67% |
|
Wrong Answer |
22 |
73.33% |
||
|
Total |
30 |
100% |
||
|
16 |
How do you record and preserve Bite Marks? |
Correct Answer |
5 |
16.67% |
|
Wrong Answer |
25 |
83.33% |
||
|
Total |
30 |
100% |
||
|
17 |
You can see Bite Marks from crime scenes. Who do analysis of this Bite Marks? |
Medical Practitioner |
39 |
29.30% |
|
Criminal Lawyer |
8 |
6.00% |
||
|
Pathologist |
8 |
6.00% |
||
|
Forensic Dental Expert |
78 |
58.60% |
|
Question Number |
Question |
Options |
Frequency |
Percentage |
|
18 |
Do you know importance of teeth preservation in Medicolegal cases? |
Yes |
75 |
56.40% |
|
No |
58 |
43.60% |
||
|
19 |
In violence incidents if you found some missing teeth in person, Do you take consultation of Dental Surgeon? |
Yes |
85 |
63.90% |
|
No |
48 |
36.10% |
|
Knowledge level of Forensic Dentistry |
Experience |
Total |
P-value |
|
|
< 10 years |
>10 years |
|||
|
Insufficient knowledge Sufficient knowledge Total |
55 (65.48%) |
13 (26.53%) |
68 (51.13%) |
< 0.001 (HS) |
|
29 (34.52%) |
36 (73.47%) |
65 (48.87%) |
|
|
|
84(100.00%) |
49 (100.00%) |
133(100.00%) |
|
|
Knowledge level of Forensic Dentistry |
Sex |
Total |
P-value |
|
|
Male |
Female |
|||
|
Insufficient knowledge Sufficient knowledge Total |
52 (47.71%) 57 (52.29%) 109 (100.00%) |
16 (66.67%) 8 (33.33%) 24 (100.00%) |
68 (51.13%) 65 (48.87%) 133 (100.00%) |
0.09 (NS) |
|
Knowledge level of Forensic Dentistry |
Rank |
Total |
P-value |
|
|
Constable |
Above from Constable |
|||
|
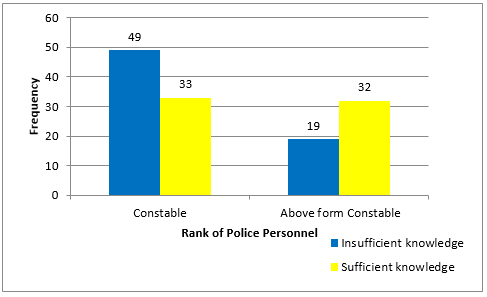
Insufficient knowledge Sufficient knowledge Total |
49 (59.76%) |
19 (37.25%) |
68 (51.13%) |
0.01 (S) |
|
33 (40.24%) |
32 (62.75%) |
65 (48.87%) |
|
|
|
82 (100.00%) |
51 (100.00%) |
133 (100.00%) |
|
|
Knowledge level of Forensic Dentistry |
Education |
Total |
P-value |
|
|
Lower from Graduation |
Graduation or Post Graduation |
|||
|
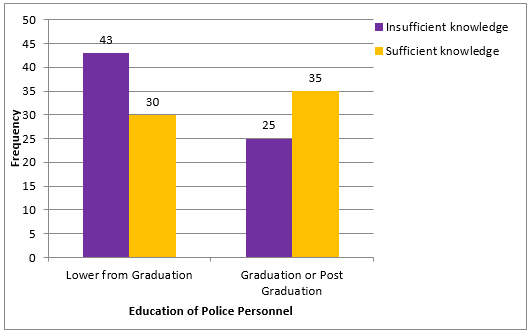
Insufficient knowledge Sufficient knowledge Total |
43 (58.90%) 30 (41.10%) 73 (100.00%) |
25 (41.67%) 35 (58.33%) 60 (100.00%) |
68 (51.13%) 65 (48.87%) 133 (100.00%) |
0.04 (S) |
Results
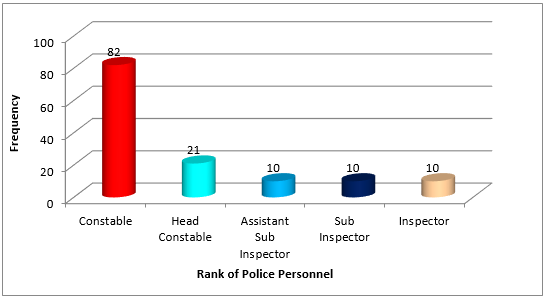
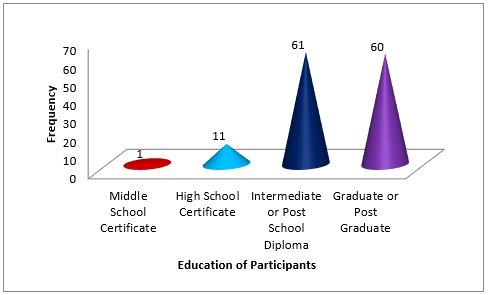
A total of 133 Police Personnel of District Police Headquarters of Mahasamund available at the time of study were included in our study. 12 Police Personnel refused to participate in study. 92% participants gave responses. The mean age of participants was 34.81 years (SD-10.93). The mean experience of Police Personnel was 11.10 years (SD-10.00). Most of the participants were Male (82.00%) in our study. Out of 133 Policemen 61.70% Constables, 15.80% Head Constables, 7.50% Assistant Sub Inspectors, 7.50% Sub Inspectors and 7.50% Inspectors were agreed to take part in survey. ([Table 1] and [Figure 1] ) In present study 45.90% participants were intermediate or post school diploma. ([Table 2] and [Figure 2])
Basic knowledge of forensic science ([Table 3] )
All participants had knowledge about Forensic Science. Majority of them (83.50%) answered that Forensic Science help is sought by Police in solving cases for investigations. In present study (82.70%) Police Personnel had awareness that Forensic Dentistry is part of Forensic Science.
Basic knowledge of forensic dentistry ([Table 4])
No participants had any formal training for evaluating dental testimony. Only (57.90%) were aware of that Forensic Odontology can be used for identification of victims. In present study (63.20%) were a view of that Forensic Odontology can be used for recognition of age and sex of victims. Only (36.10%) participants had knowledge that Forensic Odontology is useful for Age determination, D.N.A. analysis and Bite Marks.
Dental identifications ([Table 5] )
In present study 52.60% participants had enough knowledge that dental identification marks can be used for identification of victims. According to 35.20% participants saliva can be helpful for victim’s identification. Among participants, 46.60% were aware of the fact that D.N.A. analysis can be done using person’s teeth. About 41% participants gave positive nod on importance of Dental prosthesis in recognition of deceased person in Mass Disaster.
Abuse ([Table 6] )
Only (39.10%) had knowledge about importance of Dental Photography in Abuse and Domestic Violence cases.
Bite mark evidence ([Table 7])
Only 22.60% knew about Bite Marks. Out of that 46.67% reported correctly about Bite Marks. Most of them (73.33%) did not know about how Bite Marks can be helpful for solving cases. Eighty three percent participants did not aware of record and preservation of Bite Marks correctly. When multiple options were provided to them for the question, who do analysis of Bite Marks, 58.60% Police Personnel were a view of that Forensic Dental Expert do analysis of Bite Marks.
Criminal litigations ([Table 8])
Fifty six percent participants had knowledge of importance of teeth preservation in Medicolegal Cases. If violence occurs, 63.20% participants took consultation of Dental Surgeon.
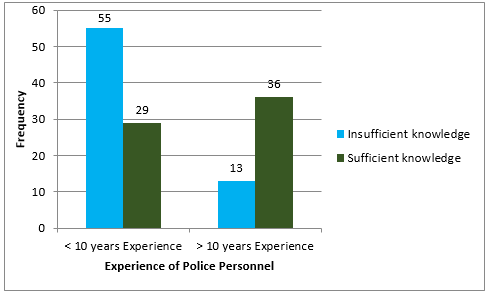
Overall knowledge of forensic dentistry among policemen according to experience ([Table 9] and [Figure 3])
Police Personnel who had more than 10 years experience had better knowledge of Forensic Dentistry. (P value < 0.001) Correct number of responses < 8 which are given by participants are considered as insufficient knowledge about Forensic Dentistry according to Experience.
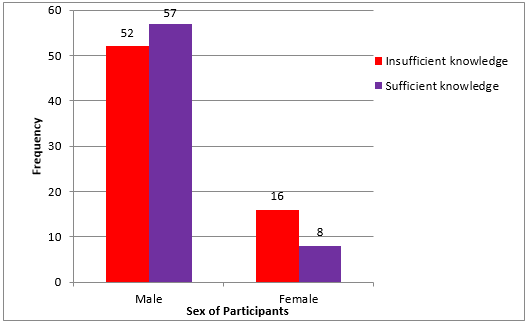
Overall knowledge of forensic dentistry among policemen according to sex ([Table 10] and [Figure 4])
There is no significant difference in knowledge of Forensic Dentistry according to sex. (P value = 0.09) Correct number of responses < 8 which are given by participants are considered as insufficient knowledge about Forensic Dentistry according to sex.
Overall knowledge of forensic dentistry among policemen according to rank ([Table 11] and [Figure 5])
Police Personnel who had rank above from Constables had more knowledge about Forensic Dentistry. (P value = 0.01) Correct number of responses < 8 which are given by participants are considered as insufficient knowledge about Forensic Dentistry according to rank.
Overall knowledge of forensic dentistry among policemen according to education ([Table 12] and [Figure 6])
Graduated or Post Graduated Police Personnel had more knowledge about Forensic Dentistry. (P value = 0.04) Correct number of responses < 8 which are given by participants are considered as insufficient knowledge about Forensic Dentistry according to Education.
Discussion
Forensic Odontology is an integral part of Forensic Science which related with proper handling and examination of dental testimony with appropriate evaluation and presentation of dental findings. Dental records can be used for identification of crime victims or accidents that are necessary for medicolegal cases. It also includes detection and assessment of severity of injuries of teeth and its Bite Marks. D.N.A. analysis of teeth pulp is useful in identification of corpses also. Bite Marks which are left by criminal on victim’s body or any innate objects like glasses on the crime scene can give clue for identification of criminal. D.N.A, analysis of saliva left on Bite Marks has a lot of importance.
Teeth had been used for identification of individual from 66 A.D., it has been said that Nero’s mistress Sabina got his wife killed by her soldiers. She recognized his wife by black anterior teeth. Dental Testimony was first accepted in court of United States of America of Webster-Parkman case in 1849. Dr. Oscar Amoeda, who is father of Forensic Odontology identified 126 victims of a fire accident of Le Bazaar de la Charite in Paris in 1897. Antemortem dental records were compared with Postmortem dental records for identification of victims. Baggi described in 1977 that dead bodies of Hitler and his mistress Eva Brauma were identified by his dental surgeon using dental testimony.
Forensic odontology had decisive role in the investigation of criminal acts like World Trade Centre New York tragedy on 11 September 2001 and terrorist incident in Bali which happened in October 2002. It has significant role in transport accidents such as Yogyakarta aircrash of 2007 and the “Black Saturday” bushfires of February 2009.26
At present there have been localized natural disasters and terrorist acts which have highlighted Forensic Odontology within forensic science, police departments and wider community. Forensic Dentistry helps a lot to Police Personnel in identification of Disaster victims, when Tsunami came in the Indian Ocean on 26 December 2004 in Thailand. Disaster Victims Identification Teams of 30 countries involved in identification of dead body. They did remarkable job for identification of deceased person and assisted Policemen.[26] Policemen reach first crime scene and do their investigation. The Policemen should have enough knowledge in identification individual’s age and sex by teeth, Bite Marks, Dental Photography and DNA analysis using teeth.
The belgiam disaster victim identification team also assists with the identification of victims of mass disasters (natural, accidental, and mass murders). They consider the contributions of different teams (forensic pathology, anthropology, odontology, federal police, and crime scene investigation) both on the scene of the attack at the Brussels National Airport (Zaventem) in 2016.
This study shows finding that Police Personnel with more than 10 years experience had better knowledge of Forensic Dentistry. (P value < 0.001) They got more number of handling general cases and encountering a variety of cases.
There had no significant difference in knowledge of Forensic Dentistry according to sex. (P value > 0.09) This can be explained that Male Police Personnel and Female Police Personnel had same training experience, similar qualification and same intelligent quotient. ,.
Our study has striking finding that Head Constables, Assistant Sub Inspectors, Sub Inspectors and Inspectors had more knowledge about Forensic Dentistry than Constables. (P value = 0.01) This indicated that they were more involved in solving cases. One study done by Sharma et al. showed that About 68.7% of high‑rank officers had essential information that dental evidence could be used as extraordinary biological testimony in the context of law.5
Graduated or Postgraduated Police Personnel had better knowledge of Forensic Dentistry. (P value = 0.04) This suggested that Education influences knowledge of Forensic Dentistry among Police Personnel.
In our study, 82% Policemen were males. This shows Police Profession is mainly dominated by Males. Woman Police Personnel continues to be negligible in Police Department in India.
Our study included only those Police Personnel who were present on day of study and willing to participate. Many Police Personnel who went outside from District Police Headquarter for doing their duty could not able to participate in study. This is limitation of our study.
Policemen who have less knowledge of Forensic Odontology will be unable to skillfully assess and handle scientific testimony which leads to factual errors. Majority of criminal cases, conflicts, natural and man‑made disasters dealt by the Policemen. Usually they do not involve active participation of forensic dental experts.28 Pandit et al. also displayed that there should be requirement for better communication between the Policemen and Forensic Odontologists.6 Mansour Al‑Sarhani‑endorsed use of Forensic Odontology in criminal probes to identify the suspects and victims.29 Rahmat et al. also implied that Policemen could be educated through structured continuing education programs.30 The traditional Police Training does not include basic concepts in Forensic Odontology right now. Essential scientific concepts about Forensic Odontology can be incorporated and that practical internship can also be included for Policemen so that they can able to independently solving cases in Forensic Odontology.
Recommendations
There is urgency of training of Policemen regarding Forensic Odontology in India.
Continuing Dental Education Program might be done by Dental Colleges in India for Policeman.
For Mass Disaster Manpower strength available should be established. These should include local personnel, Policemen, transportation companies as well as specialists such as forensic odontologists, forensic pathologists, forensic anthropologists and fingerprints specialists etc.
Referral centers should be established with well-equipped dental labs at least at the district levels, standardization of techniques and improvements in record keeping is very important.
Conclusion
This study revealed that most of the Policemen had inadequate knowledge about Forensic Dentistry. This study shows current status of our country in the field of Forensic Odontology. Forensic Dentistry helps Policemen and judges in the law court to reconstruct truth from tooth. A good knowledge on Forensic Odontology in crime scenes are requisite for Policemen to provide timely justice to everyone.
Forensic Odontology can help very much to Policemen. Although Policemen are given knowledge about medicolegal cases, but further reorientation about Forensic Dentistry is very much required. If they have sufficient knowledge regarding Forensic Odontology, they can efficiently work in solving criminal cases and in mass disasters.
Source of Funding
The author did not receive support from any organization for the submitted work. There was no funding to assist with the preparation of this manuscript.
Conflict of Interest
None.
Ethics Approval
Ethical Approval was taken from Institutional Review Board Rungta Dental College, Bhilai
References
- . Forensic Science, National Institute of Standards and Technology. . [Google Scholar]
- AO Amankwaa, EN Amoako, D Bonsu, M Banyeh. Forensic science in Ghana: A review. J Forensic Sci Int 2019. [Google Scholar]
- C Shekar, BR Reddy. Role of dentists in person identification. Indian J Dent Res 2009. [Google Scholar]
- . Explained| The clogged state of the Indian judiciary. The Hindu. . [Google Scholar]
- D Sharma, G Koshy, A Pabla, S Garg, M Singh. An insight into the awareness and utilization of “dental evidence” among the police force in Punjab. J Forensic Dent Sci 2018. [Google Scholar]
- S Pandit, D Desai, P Jeergal, S Venkatesh. Awareness of forensic odontology among police personnel: A new ray of hope in forensic odontology. J Forensic Dent Sci 2016. [Google Scholar]
- E Choudhary, A Vashisht, A Kulshreshta, P Jain, S Chand, K Dhanker. An Insight into the Awareness and Utilization of Dental Evidence Among the Police Force in Greater Noida. Ann R.S.C.B 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ass Patel, AS Saxena, AD Ikhar, RD Bhede, HD Saraf. Forensic Odontology at a Glance. Int J Dent Clin 2013. [Google Scholar]
- N Harchandani, S Marathe, M Hebbale, SU Nisa, D Hiremutt. Awareness of Forensic Odontology among General Dental Practitioners in Pune - A Cross-sectional Study. J Adv Med Dent Scie Res 2014. [Google Scholar]
- JM Jayakrishnan, J Reddy, RB Kumar. Role of forensic odontology and anthropology in the identification of human remains. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol 2021. [Google Scholar]
- A Kurniawan, A Chusida, N Atika, TK Gianosa, MD Solikhin, MS Margaretha. The Applicable Dental Age Estimation Methods for Children and Adolescents in Indonesia. Int J Dent 2022. [Google Scholar]
- AA Gupta, S Kheur, A Alshehri, W Awadh, ZH Ahmed. Is Palatal Rugae Pattern a Reliable Tool for Personal Identification following Orthodontic Treatment? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics 2022. [Google Scholar]
- M Yazdanian, S Karami, E Tahmasebi, M Alam, K Abbasi, M Rahbar. Dental Radiographic/Digital Radiography Technology along with Biological Agents in Human Identification. J Scanning 2022. [Google Scholar]
- G Sujatha, VV Priya, A Dubey, S Mujoo, AM Sulimany, O Tawhari. Toothbrushes as a Source of DNA for Gender and Human Identification-A Systematic Review. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2021. [Google Scholar]
- JL Bukyya, M Tejasvi, A Avinash, HP Chanchala, P Talwade, MM Afroz. DNA Profiling in Forensic Science: A Review.. Glob Med Genet 2021. [Google Scholar]
- AK Verma, S Kumar, S Rathore, A Pandey. Role of dental expert in forensic odontology. Natl J Maxillofac Surg 2014. [Google Scholar]
- S Indu, VS Cheema, B Jayan, R Mitra, D Chaudhary. Forensic odontology: An inseparable aspect of military dentistry. J Dent Def Sect 2021. [Google Scholar]
- G Prajapati, SC Sarode, GS Sarode, P Shelke, KH Awan, S Patil. Role of forensic odontology in the identification of victims of major mass disasters across the world: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2018. [Google Scholar]
- J Zwirner, W Dunacn. A disaster victim identification workshop focused on forensic odontology using embalmed human remains. Int J Legal Med 2022. [Google Scholar]
- A Forrest. Forensic odontology in DVI: current practice and recent advances. Forens Sci Res 2019. [Google Scholar]
- S Sengupta, V Sharma, V Gupta, H Vij, R Vij, K Prabhat. Forensic Odontology as a victim identification tool in mass disaster: A feasibility study in Indian scenario. J Forensic Dent Sci 2014. [Google Scholar]
- S Preeti, A Einstein, B Sivapathasundharam. Awareness of forensic odontology among dental practitioners in Chennai: A knowledge, attitude and practice survey. J Forensic Dent Sci 2011. [Google Scholar]
- . Nirbhaya case: Dharwad college helped with forensic analysis. The Times of India. 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sheena Bora Case. . How skull-face superimposition process identified remains. The Times of India 2015. [Google Scholar]
- B Kumar, NP Singh, N Singh, N Goel. Importance of Crime Scene Visits by a Forensic Medicine Expert: A Survey-Based Study. J Cureus 2022. [Google Scholar]
- P Shetty, A Raviprakash. Forensic odontology in India, an oral pathologist's perspective. J Forensic Dent Sci 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Introduction
- Materials and Methods
- Results
- Basic knowledge of forensic science ([Table 3] )
- Basic knowledge of forensic dentistry ([Table 4])
- Dental identifications ([Table 5] )
- Abuse ([Table 6] )
- Bite mark evidence ([Table 7])
- Criminal litigations ([Table 8])
- Overall knowledge of forensic dentistry among policemen according to experience ([Table 9] and [Figure 3])
- Overall knowledge of forensic dentistry among policemen according to sex ([Table 10] and [Figure 4])
- Overall knowledge of forensic dentistry among policemen according to rank ([Table 11] and [Figure 5])
- Overall knowledge of forensic dentistry among policemen according to education ([Table 12] and [Figure 6])
- Discussion
- Conclusion
- Source of Funding
- Conflict of Interest
- Ethics Approval
